Convex & Clerk
Clerk is an authentication platform providing login via passwords, social identity providers, one-time email or SMS access codes, and multi-factor authentication and user management.
Get started
Convex offers a provider that is specifically for integrating with Clerk called
<ConvexProviderWithClerk>. It works with any of Clerk's React-based SDKs, such
as the Next.js and Expo SDKs.
See the following sections for the Clerk SDK that you're using:
- React - Use this as a starting point if your SDK is not listed
- Next.js
- TanStack Start
React
Example: React with Convex and Clerk
This guide assumes you already have a working React app with Convex. If not follow the Convex React Quickstart first. Then:
- Sign up for Clerk
Sign up for a free Clerk account at clerk.com/sign-up.
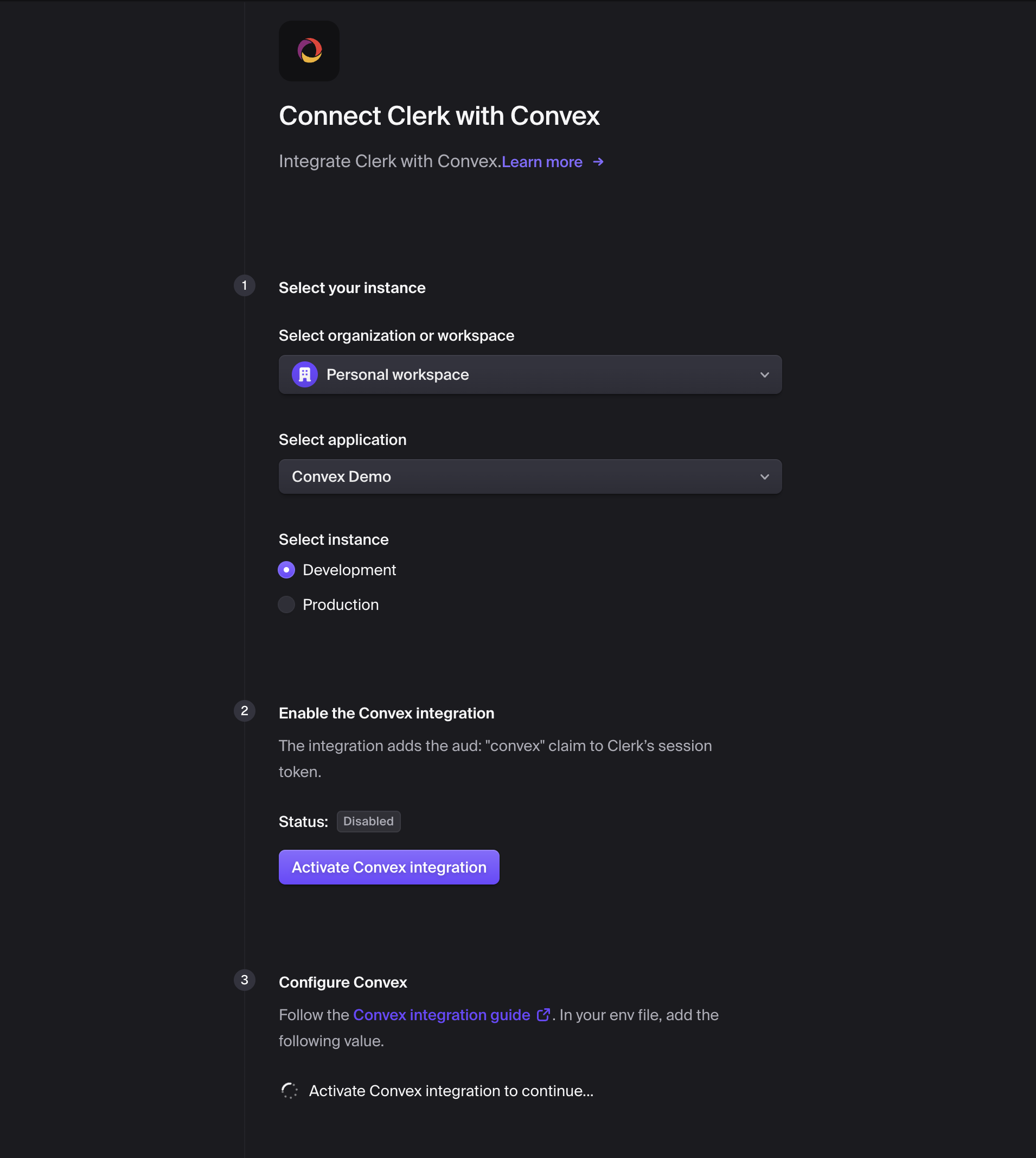
- Create an application in Clerk
Choose how you want your users to sign in.
Copy your Clerk app's Frontend API URL. In development, its format will be
https://verb-noun-00.clerk.accounts.dev. In production, its format will behttps://clerk.<your-domain>.com.- Configure Convex with the Clerk issuer domain
In your app's
convexfolder, create a new fileauth.config.tswith the following code. This is the server-side configuration for validating access tokens.convex/auth.config.tsTSimport { AuthConfig } from "convex/server";
export default {
providers: [
{
// Replace with your Clerk Frontend API URL
// or with `process.env.CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN`
// and configure CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN on the Convex Dashboard
// See https://docs.convex.dev/auth/clerk#configuring-dev-and-prod-instances
domain: process.env.CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN!,
applicationID: "convex",
},
]
} satisfies AuthConfig; - Deploy your changes
Run
npx convex devto automatically sync your configuration to your backend.npx convex dev - Install clerk
In a new terminal window, install the Clerk React SDK:
npm install @clerk/clerk-react - Set your Clerk API keys
In the Clerk Dashboard, navigate to the API keys page. In the Quick Copy section, copy your Clerk Publishable Key and set it as the
CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEYenvironment variable. If you're using Vite, you will need to prefix it withVITE_..envVITE_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY=YOUR_PUBLISHABLE_KEY - Configure ConvexProviderWithClerk
Both Clerk and Convex have provider components that are required to provide authentication and client context.
You should already have
<ConvexProvider>wrapping your app. Replace it with<ConvexProviderWithClerk>, and pass Clerk'suseAuth()hook to it.Then, wrap it with
<ClerkProvider>.<ClerkProvider>requires apublishableKeyprop, which you can set to theVITE_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEYenvironment variable.src/main.tsxTSimport React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./App";
import "./index.css";
import { ClerkProvider, useAuth } from "@clerk/clerk-react";
import { ConvexProviderWithClerk } from "convex/react-clerk";
import { ConvexReactClient } from "convex/react";
const convex = new ConvexReactClient(import.meta.env.VITE_CONVEX_URL as string);
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")!).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<ClerkProvider publishableKey="pk_test_...">
<ConvexProviderWithClerk client={convex} useAuth={useAuth}>
<App />
</ConvexProviderWithClerk>
</ClerkProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
); - Show UI based on authentication state
You can control which UI is shown when the user is signed in or signed out using Convex's
<Authenticated>,<Unauthenticated>and<AuthLoading>helper components. These should be used instead of Clerk's<SignedIn>,<SignedOut>and<ClerkLoading>components, respectively.It's important to use the
useConvexAuth()hook instead of Clerk'suseAuth()hook when you need to check whether the user is logged in or not. TheuseConvexAuth()hook makes sure that the browser has fetched the auth token needed to make authenticated requests to your Convex backend, and that the Convex backend has validated it.In the following example, the
<Content />component is a child of<Authenticated>, so its content and any of its child components are guaranteed to have an authenticated user, and Convex queries can require authentication.src/App.tsxTSimport { SignInButton, UserButton } from "@clerk/clerk-react";
import { Authenticated, Unauthenticated, AuthLoading, useQuery } from "convex/react";
import { api } from "../convex/_generated/api";
function App() {
return (
<main>
<Unauthenticated>
<SignInButton />
</Unauthenticated>
<Authenticated>
<UserButton />
<Content />
</Authenticated>
<AuthLoading>
<p>Still loading</p>
</AuthLoading>
</main>
);
}
function Content() {
const messages = useQuery(api.messages.getForCurrentUser);
return <div>Authenticated content: {messages?.length}</div>;
}
export default App; - Use authentication state in your Convex functions
If the client is authenticated, you can access the information stored in the JWT via
ctx.auth.getUserIdentity.If the client isn't authenticated,
ctx.auth.getUserIdentitywill returnnull.Make sure that the component calling this query is a child of
<Authenticated>fromconvex/react. Otherwise, it will throw on page load.convex/messages.tsTSimport { query } from "./_generated/server";
export const getForCurrentUser = query({
args: {},
handler: async (ctx) => {
const identity = await ctx.auth.getUserIdentity();
if (identity === null) {
throw new Error("Not authenticated");
}
return await ctx.db
.query("messages")
.withIndex("by_author", (q) => q.eq("author", identity.email))
.collect();
},
});
Next.js
Example: Next.js with Convex and Clerk
This guide assumes you already have a working Next.js app with Convex. If not follow the Convex Next.js Quickstart first. Then:
- Sign up for Clerk
Sign up for a free Clerk account at clerk.com/sign-up.

- Create an application in Clerk
Choose how you want your users to sign in.

Copy your Clerk app's Frontend API URL. In development, its format will be
https://verb-noun-00.clerk.accounts.dev. In production, its format will behttps://clerk.<your-domain>.com.- Configure Convex with the Clerk issuer domain
In your app's
convexfolder, create a new fileauth.config.tswith the following code. This is the server-side configuration for validating access tokens.convex/auth.config.tsTSimport { AuthConfig } from "convex/server";
export default {
providers: [
{
// Replace with your Clerk Frontend API URL
// or with `process.env.CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN`
// and configure CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN on the Convex Dashboard
// See https://docs.convex.dev/auth/clerk#configuring-dev-and-prod-instances
domain: process.env.CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN!,
applicationID: "convex",
},
]
} satisfies AuthConfig; - Deploy your changes
Run
npx convex devto automatically sync your configuration to your backend.npx convex dev - Install clerk
In a new terminal window, install the Clerk Next.js SDK:
npm install @clerk/nextjs - Set your Clerk API keys
In the Clerk Dashboard, navigate to the API keys page. In the Quick Copy section, copy your Clerk Publishable and Secret Keys and set them as the
NEXT_PUBLIC_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEYandCLERK_SECRET_KEYenvironment variables, respectively..envNEXT_PUBLIC_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY=YOUR_PUBLISHABLE_KEY
CLERK_SECRET_KEY=YOUR_SECRET_KEY - Add Clerk middleware
Clerk's
clerkMiddleware()helper grants you access to user authentication state throughout your app.Create a
middleware.tsfile.In your
middleware.tsfile, export theclerkMiddleware()helper:import { clerkMiddleware } from '@clerk/nextjs/server'
export default clerkMiddleware()
export const config = {
matcher: [
// Skip Next.js internals and all static files, unless found in search params
'/((?!_next|[^?]*\\.(?:html?|css|js(?!on)|jpe?g|webp|png|gif|svg|ttf|woff2?|ico|csv|docx?|xlsx?|zip|webmanifest)).*)',
// Always run for API routes
'/(api|trpc)(.*)',
],
}By default,
clerkMiddleware()will not protect any routes. All routes are public and you must opt-in to protection for routes.https://clerk.com/docs/references/nextjs/clerk-middleware) to learn how to require authentication for specific routes. - Configure ConvexProviderWithClerk
Both Clerk and Convex have provider components that are required to provide authentication and client context.
Typically, you'd replace
<ConvexProvider>with<ConvexProviderWithClerk>, but with Next.js App Router, things are a bit more complex.<ConvexProviderWithClerk>callsConvexReactClient()to get Convex's client, so it must be used in a Client Component. Yourapp/layout.tsx, where you would use<ConvexProviderWithClerk>, is a Server Component, and a Server Component cannot contain Client Component code. To solve this, you must first create a wrapper Client Component around<ConvexProviderWithClerk>.'use client'
import { ReactNode } from 'react'
import { ConvexReactClient } from 'convex/react'
import { ConvexProviderWithClerk } from 'convex/react-clerk'
import { useAuth } from '@clerk/nextjs'
if (!process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_CONVEX_URL) {
throw new Error('Missing NEXT_PUBLIC_CONVEX_URL in your .env file')
}
const convex = new ConvexReactClient(process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_CONVEX_URL)
export default function ConvexClientProvider({ children }: { children: ReactNode }) {
return (
<ConvexProviderWithClerk client={convex} useAuth={useAuth}>
{children}
</ConvexProviderWithClerk>
)
} - Wrap your app in Clerk and Convex
Now, your Server Component,
app/layout.tsx, can render<ConvexClientProvider>instead of rendering<ConvexProviderWithClerk>directly. It's important that<ClerkProvider>wraps<ConvexClientProvider>, and not the other way around, as Convex needs to be able to access the Clerk context.import type { Metadata } from 'next'
import { Geist, Geist_Mono } from 'next/font/google'
import './globals.css'
import { ClerkProvider } from '@clerk/nextjs'
import ConvexClientProvider from '@/components/ConvexClientProvider'
const geistSans = Geist({
variable: '--font-geist-sans',
subsets: ['latin'],
})
const geistMono = Geist_Mono({
variable: '--font-geist-mono',
subsets: ['latin'],
})
export const metadata: Metadata = {
title: 'Clerk Next.js Quickstart',
description: 'Generated by create next app',
}
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: Readonly<{
children: React.ReactNode
}>) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body className={`${geistSans.variable} ${geistMono.variable} antialiased`}>
<ClerkProvider>
<ConvexClientProvider>{children}</ConvexClientProvider>
</ClerkProvider>
</body>
</html>
)
} - Show UI based on authentication state
You can control which UI is shown when the user is signed in or signed out using Convex's
<Authenticated>,<Unauthenticated>and<AuthLoading>helper components. These should be used instead of Clerk's<SignedIn>,<SignedOut>and<ClerkLoading>components, respectively.It's important to use the
useConvexAuth()hook instead of Clerk'suseAuth()hook when you need to check whether the user is logged in or not. TheuseConvexAuth()hook makes sure that the browser has fetched the auth token needed to make authenticated requests to your Convex backend, and that the Convex backend has validated it.In the following example, the
<Content />component is a child of<Authenticated>, so its content and any of its child components are guaranteed to have an authenticated user, and Convex queries can require authentication.app/page.tsxTS"use client";
import { Authenticated, Unauthenticated } from "convex/react";
import { SignInButton, UserButton } from "@clerk/nextjs";
import { useQuery } from "convex/react";
import { api } from "../convex/_generated/api";
export default function Home() {
return (
<>
<Authenticated>
<UserButton />
<Content />
</Authenticated>
<Unauthenticated>
<SignInButton />
</Unauthenticated>
</>
);
}
function Content() {
const messages = useQuery(api.messages.getForCurrentUser);
return <div>Authenticated content: {messages?.length}</div>;
} - Use authentication state in your Convex functions
If the client is authenticated, you can access the information stored in the JWT via
ctx.auth.getUserIdentity.If the client isn't authenticated,
ctx.auth.getUserIdentitywill returnnull.Make sure that the component calling this query is a child of
<Authenticated>fromconvex/react. Otherwise, it will throw on page load.convex/messages.tsTSimport { query } from "./_generated/server";
export const getForCurrentUser = query({
args: {},
handler: async (ctx) => {
const identity = await ctx.auth.getUserIdentity();
if (identity === null) {
throw new Error("Not authenticated");
}
return await ctx.db
.query("messages")
.withIndex("by_author", (q) => q.eq("author", identity.email))
.collect();
},
});
TanStack Start
Example: TanStack Start with Convex and Clerk
See the TanStack Start with Clerk guide for more information.
Next steps
Accessing user information in functions
See Auth in Functions to learn about how to access information about the authenticated user in your queries, mutations and actions.
See Storing Users in the Convex Database to learn about how to store user information in the Convex database.
Accessing user information client-side
To access the authenticated user's information, use Clerk's User object, which
can be accessed using Clerk's
useUser() hook. For more information
on the User object, see the
Clerk docs.
export default function Badge() {
const { user } = useUser();
return <span>Logged in as {user.fullName}</span>;
}
Configuring dev and prod instances
To configure a different Clerk instance between your Convex development and production deployments, you can use environment variables configured on the Convex dashboard.
Configuring the backend
In the Clerk Dashboard, navigate to the
API keys page. Copy
your Clerk Frontend API URL. This URL is the issuer domain necessary for Convex
to validate access tokens. In development, it's format will be
https://verb-noun-00.clerk.accounts.dev. In production, it's format will be
https://clerk.<your-domain>.com.
Paste your Clerk Frontend API URL into your .env file, set it as the
CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN environment variable.
CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN=https://verb-noun-00.clerk.accounts.dev
Then, update your auth.config.ts file to use the
environment variable.
import { AuthConfig } from "convex/server";
export default {
providers: [
{
domain: process.env.CLERK_JWT_ISSUER_DOMAIN!,
applicationID: "convex",
},
],
} satisfies AuthConfig;
Development configuration
In the left sidenav of the Convex dashboard, switch to your development deployment and set the values for your development Clerk instance.
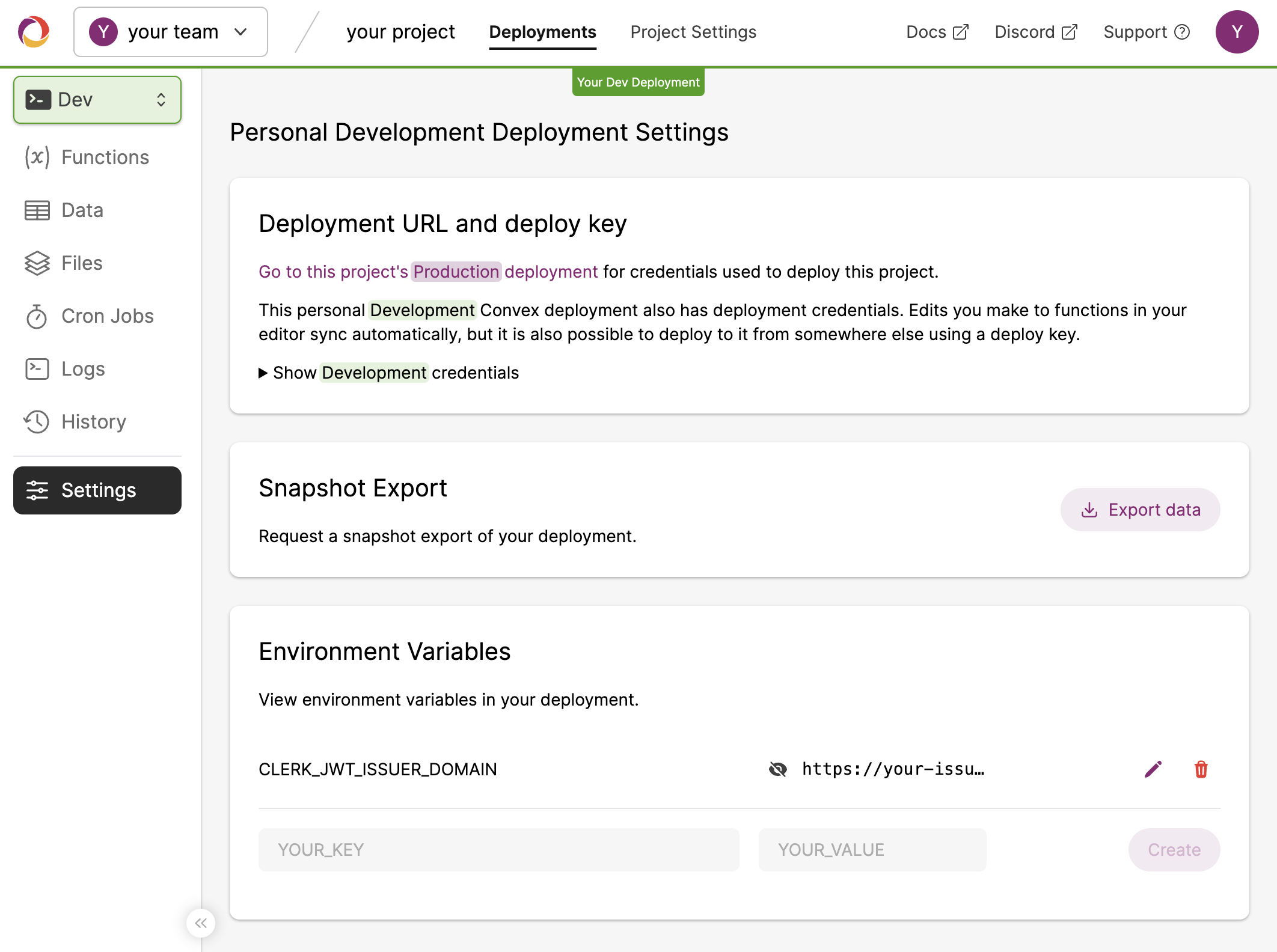
Then, to switch your deployment to the new configuration, run npx convex dev.
Production configuration
In the left sidenav of the Convex dashboard, switch to your production deployment and set the values for your production Clerk instance.
Then, to switch your deployment to the new configuration, run
npx convex deploy.
Configuring Clerk's API keys
Clerk's API keys differ depending on whether they are for development or
production. Don't forget to update the environment variables in your .env file
as well as your hosting platform, such as Vercel or Netlify.
Development configuration
Clerk's Publishable Key for development follows the format pk_test_....
VITE_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY="pk_test_..."
Production configuration
Clerk's Publishable Key for production follows the format pk_live_....
NEXT_PUBLIC_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY="pk_live_..."
Debugging authentication
If a user goes through the Clerk login flow successfully, and after being
redirected back to your page, useConvexAuth() returns
isAuthenticated: false, it's possible that your backend isn't correctly
configured.
The auth.config.ts file contains a list of
configured authentication providers. You must run npx convex dev or
npx convex deploy after adding a new provider to sync the configuration to
your backend.
For more thorough debugging steps, see Debugging Authentication.
Under the hood
The authentication flow looks like this under the hood:
- The user clicks a login button
- The user is redirected to a page where they log in via whatever method you configure in Clerk
- After a successful login Clerk redirects back to your page, or a
different page which you configure via the
afterSignInprop. - The
ClerkProvidernow knows that the user is authenticated. - The
ConvexProviderWithClerkfetches an auth token from Clerk. - The
ConvexReactClientpasses this token down to your Convex backend to validate - Your Convex backend retrieves the public key from Clerk to check that the token's signature is valid.
- The
ConvexReactClientis notified of successful authentication, andConvexProviderWithClerknow knows that the user is authenticated with Convex.useConvexAuthreturnsisAuthenticated: trueand theAuthenticatedcomponent renders its children.
ConvexProviderWithClerk takes care of refetching the token when needed to
make sure the user stays authenticated with your backend.